Reconciliation Processes: Step-by-Step Guide

Finance reconciliation is a process that all businesses know very well. To ensure the accuracy of financial statements, businesses must perform a financial reconciliation. This can be done manually, but its time-consuming nature and intense attention to detail make a reconciliation process well-suited for automation.
While each business performs financial reconciliation on its schedule, most follow the same steps. Here, we will explore everything you need to know about account reconciliation, from the definition to the steps to how automation can help.
What is Reconciliation?
Reconciliation is the process of comparing your internal financial records against external statements—such as bank statements, invoices, or credit card bills—to ensure they match and identify any discrepancies.
This verification process is foundational in accounting. Every accurate financial statement, audit, and business decision depends on reconciled accounts. Without regular reconciliation, businesses risk making decisions based on incomplete or incorrect financial data.
Key Takeaways:
- Reconciliation in accounting verifies that internal records align with external sources
- The reconciliation process applies to multiple account types: bank accounts, accounts payable, accounts receivable, credit cards, and general ledger accounts
- Regular account reconciliation prevents financial misstatements and catches errors before they cascade into larger problems
- Timing differences between records are normal; unexplained discrepancies require investigation
- For public companies, reconciliation processes are legally mandated internal controls
Financial reconciliation ensures that money entering and leaving your accounts is accurately documented. Most companies perform general ledger reconciliation as their primary process, though reconciliation in accounting extends across all account types—from bank reconciliation to vendor payments to customer receivables. The reconciliation process serves as your first line of defense against financial misstatements, catching errors, fraud, and discrepancies before they impact reporting or decision-making.
Not every discrepancy signals a problem. Timing differences occur naturally—like a deposit you've recorded that hasn't yet appeared on your bank statement. However, unexplained differences require immediate investigation, as they could indicate errors, system issues, or fraudulent activity. For public companies, reconciliation isn't optional. It's a mandated internal control that must be completed before financial close. Errors can trigger compliance violations, restatements, and regulatory penalties, which is why reconciliation processes must meet strict accuracy standards.
Reconciliation vs. Account Reconciliation
While the terms are often used interchangeably, account reconciliation is actually a subset of the broader reconciliation process. Understanding this distinction helps businesses implement more comprehensive financial controls.
Reconciliation is the umbrella term for any process that compares and verifies financial data across different sources. This includes account reconciliation but extends to other verification processes like intercompany reconciliation (matching transactions between subsidiaries or business units to eliminate duplicate reporting) and tax reconciliation (verifying that tax liabilities recorded in financial statements match amounts filed with tax authorities).
Account reconciliation specifically focuses on verifying individual accounts by comparing internal ledgers against external statements. The most common examples are bank reconciliation—where you match your cash account balance with your bank statement to identify outstanding checks or deposits in transit—and credit card reconciliation, where you verify that all corporate card charges in your accounting system align with the credit card statement.
Both types of reconciliation serve the same fundamental purpose: ensuring accuracy and catching discrepancies. However, account reconciliation typically happens more frequently (often monthly) and focuses on transactional accuracy, while broader reconciliation processes may occur quarterly or annually and address systemic or cross-entity issues.

Why Reconciliation Processes Matter in Accounting
Reconciliation processes are essential to maintaining accurate financial records and ensuring business health. Beyond simply verifying numbers, reconciliation in accounting directly impacts your ability to close books confidently, analyze cash flow accurately, prepare for tax filings, and demonstrate audit readiness when regulators or stakeholders come calling.
Every critical financial process depends on reconciled accounts. Your monthly close can't be finalized until reconciliation confirms all accounts balance correctly. Cash flow analysis relies on accurate bank reconciliation to show true liquidity. Tax preparation requires reconciled records to support deductions and ensure compliance. Without regular reconciliation, these fundamental business processes become unreliable, exposing your company to financial risk and regulatory scrutiny.
For public companies, reconciliation isn't optional—it's a mandated internal control. Independent auditors scrutinize reconciliation processes during financial statement audits, and inadequate practices can result in qualified opinions, compliance violations, and serious penalties. Even private businesses benefit from treating reconciliation as non-negotiable, as it protects against errors that could lead to poor decisions or financial losses.
Benefits of Regular Reconciliation
Financial reconciliation delivers tangible benefits that protect your bottom line and improve operational efficiency. The reconciliation process catches issues early when they're easiest and least expensive to fix.
Timely error detection is one of the most valuable benefits of account reconciliation. Regular reconciliation identifies double payments before vendors cash checks, catches missed payments before they become late fees or damage vendor relationships, and spots data entry errors before they multiply across financial statements. The sooner you detect an error, the less it costs to correct—both financially and in terms of staff time.
Accurate data drives better decision-making. When you reconcile accounts regularly, leadership can trust the numbers they're using to make strategic decisions. Whether evaluating a new investment, determining budget allocations, or assessing profitability, reconciled financial records provide the reliable foundation executives need. Making decisions based on unreconciled books is like navigating with a broken compass—you might move forward, but you're likely headed in the wrong direction.
Stronger internal controls emerge naturally from consistent reconciliation processes. When employees know that accounts are reconciled regularly, it creates accountability and deters careless mistakes or intentional misconduct. The reconciliation process establishes a system of checks and balances where multiple people review financial activity, reducing the risk of errors or fraud going undetected.
Cost savings add up quickly through reconciliation. Catching duplicate vendor payments saves hard dollars that can be recovered. Identifying bank fees or incorrect charges means you can dispute them while documentation is fresh. Spotting unauthorized transactions early limits financial exposure. These direct cost savings often exceed the investment in reconciliation resources, making it a financially sound practice beyond its compliance benefits.
Compliance, Fraud Prevention & Accuracy
Reconciliation processes are fundamental to meeting accounting standards and regulatory requirements. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) require that financial statements be prepared from accurate, reconciled records. International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) mandate similar verification processes for global companies. For public companies, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) specifically requires strong internal controls over financial reporting—and regular account reconciliation is a cornerstone of SOX compliance.
Frequent reconciliation deters fraud by creating multiple verification points where irregularities surface. Fraudulent transactions often rely on going unnoticed long enough to become buried in historical records. When you perform bank reconciliation monthly, unauthorized transfers stand out immediately. When vendor reconciliation happens regularly, fictitious invoices or kickback schemes become apparent before significant damage occurs. The reconciliation process creates transparency that makes fraud both harder to commit and easier to detect.
The real-world consequences of inadequate reconciliation can be severe. Companies that fail to maintain proper reconciliation processes face qualified audit opinions that damage investor confidence, regulatory fines from bodies like the SEC for financial misstatements, restatement of financial results that erode credibility, and legal liability if fraud occurs due to weak controls. In extreme cases, executives can face personal liability under SOX for certifying inaccurate financial statements. These consequences make robust reconciliation processes not just good practice—but essential risk management.
Step-by-Step Reconciliation Process
Every business—from small startups to Fortune 500 companies—can follow this step-by-step reconciliation process to ensure accurate financial records. While the volume and complexity may vary, the fundamental steps remain consistent across organizations of all sizes.
Step 1 – Gather Financial Documents
Begin by collecting all relevant financial documents for the period you're reconciling. This includes:
- Bank statements
- Credit card statements
- Vendor invoices and bills
- Customer receipts and payment records
- General ledger reports
- Internal transaction registers
- Any other relevant financial records
Having everything assembled before you start makes the reconciliation process more efficient and reduces the risk of missing important transactions.
Pro tip: Automate document gathering through integrated accounting systems. Software like Solvexia can pull bank statements directly through APIs, import credit card transactions automatically, and consolidate data from multiple sources into a single platform. This eliminates manual downloading and reduces the risk of working with outdated information.
Step 2 – Match Internal and External Records
Compare your internal financial records against external statements line by line. Each transaction in your accounting system should have a corresponding entry in your bank statement, credit card bill, or vendor invoice. Mark off matching transactions as you verify them, working systematically through both sets of records.
Tools like Excel spreadsheets work for basic reconciliation, but accounting software streamlines the process with automated matching algorithms. These platforms can flag potential matches and highlight discrepancies, significantly reducing manual effort. Common reconciliation challenges that surface during this step include:
- Duplicate entries: A single transaction recorded twice in your system
- Missing entries: Transactions that appear in one record but not the other
- Incorrect amounts: Recorded amounts that don't match actual charges or payments
- Misclassified transactions: Entries categorized in the wrong account
Step 3 – Investigate and Adjust
Once you've identified discrepancies, determine whether they're explainable or unexplainable.
Explainable discrepancies have legitimate causes and don't indicate errors:
- Timing delays: Checks issued that haven't cleared yet, or deposits in transit
- Outstanding transactions: Payments or receipts that are legitimately pending
- Bank fees or interest: Charges the bank applied that you haven't yet recorded
Unexplainable discrepancies require investigation as they may indicate errors or fraud:
- Duplicate payments: Paying the same invoice twice
- Data entry errors: Transposing numbers or recording wrong amounts
- Unauthorized transactions: Purchases or transfers you didn't approve
- Missing transactions: Payments received that were never recorded
Document every discrepancy you find and the resolution, creating a clear audit trail. This documentation proves essential during audits and helps identify patterns that might indicate systemic issues or control weaknesses.
Step 4 – Final Review and Documentation
After making all necessary adjustments, verify that your closing balances match across all records. Your adjusted internal balance should equal the external statement balance once you account for timing differences and outstanding items.
Complete these final steps:
- Record all adjusting entries in your accounting system with proper documentation
- Verify ending balances match between internal and external records
- Obtain supervisor or manager sign-off on the completed reconciliation
- Save a complete reconciliation report including:
- Starting and ending balances
- All reconciling items with explanations
- Adjusting entries made with supporting documentation
- Final reconciled balances
- Preparer and reviewer signatures with dates
Most businesses save these reports as PDFs or within their accounting software, maintaining them as part of their permanent financial records for audit purposes and compliance requirements.
Types of Reconciliation Processes
Reconciliation in accounting extends far beyond simply matching your bank account to statements. Businesses perform multiple types of reconciliation to verify accuracy across different aspects of their financial operations. Understanding these various reconciliation processes helps you build comprehensive financial controls that protect your business from errors, fraud, and compliance issues.
Bank Reconciliation
Bank reconciliation is the most common and frequently performed type of reconciliation process. It involves comparing your internal cash account records to the bank statement to ensure they align. This process verifies that all deposits, withdrawals, fees, and checks are accurately recorded in both your accounting system and the bank's records.
During bank reconciliation, you'll match:
- Deposits: Verify that all deposits recorded in your books appear on the bank statement (accounting for deposits in transit)
- Withdrawals and payments: Confirm that all payments, transfers, and ACH transactions match between records
- Bank fees: Identify and record service charges, overdraft fees, or transaction fees
- Checks: Account for outstanding checks that have been issued but haven't cleared
- Interest earned: Record any interest income credited by the bank
Modern tools have streamlined bank reconciliation significantly. Platforms like QuickBooks and Xero connect directly to bank accounts through services like Plaid, automatically importing transactions and suggesting matches. This automation reduces manual data entry and catches discrepancies faster than traditional methods. However, human review remains essential to investigate unexplained differences and ensure accuracy.
Vendor and Customer Reconciliation
Vendor reconciliation and customer reconciliation address accounts payable and accounts receivable respectively, ensuring your records match those of your business partners.
Vendor reconciliation focuses on accounts payable by comparing your payment records against vendor invoices and statements. This process verifies that you've paid the correct amounts, received proper credit for returns or discounts, and haven't made duplicate payments. Regular vendor reconciliation strengthens supplier relationships by catching payment issues before they become disputes and helps identify opportunities to take advantage of early payment discounts.
Customer reconciliation deals with accounts receivable by matching customer payments to issued invoices. This reconciliation process confirms that all payments received are properly applied, identifies overdue invoices that require collection action, and catches any customer overpayments that need to be refunded or credited. Customer reconciliation has direct implications for credit control—it helps you spot patterns of late payment that might warrant adjusting credit terms, identify customers who consistently pay early (and might warrant extended credit), and maintain accurate aging reports that inform collection strategies.
Both vendor and customer reconciliation support healthy cash flow management. When you know exactly what you owe and what's owed to you, you can make better decisions about purchasing, staffing, and growth investments.
Intercompany & Tax Reconciliation
Some reconciliation processes address more complex financial relationships and regulatory requirements.
Intercompany reconciliation ensures accurate consolidation when your business operates through multiple divisions, subsidiaries, or legal entities. This process matches transactions between related entities—such as transfers of goods, shared services, or loans—to ensure they're recorded consistently on both sides. Without proper intercompany reconciliation, consolidated financial statements can double-count revenue, misstate assets, or hide losses. For public companies, inaccurate intercompany accounting can trigger restatements and regulatory scrutiny. The stakes are high: improper consolidation can misrepresent your company's true financial position to investors, lenders, and regulators.
Tax reconciliation matches your internal tax records to amounts reported on government filings, including sales tax, income tax, payroll tax, and other tax liabilities. This reconciliation process verifies that tax payments made throughout the year align with your actual tax liability and that all required filings are accurate and complete. Tax reconciliation is critical because errors can result in penalties, interest charges, audits by tax authorities, loss of deductions or credits due to poor documentation, and in severe cases, accusations of tax evasion or fraud.
Both intercompany and tax reconciliation require meticulous attention to detail and strong documentation practices. The legal and financial penalties for errors in these areas far exceed typical accounting mistakes, making them essential components of a comprehensive reconciliation strategy.
Manual Reconciliation vs. Automated Reconciliation Tools
Despite technological advances, many companies still perform financial reconciliation using Excel spreadsheets and manual processes. While this approach can work for simple scenarios, businesses increasingly recognize that automated reconciliation tools offer significant advantages in accuracy, efficiency, and control. Understanding when to use each approach helps you make informed decisions about your reconciliation processes.
Advantages of Automation
Automated reconciliation tools transform the reconciliation process from a time-consuming manual task into an efficient, accurate operation that strengthens financial controls.
- Time savings represent the most immediate benefit of automation. What once took days of manual matching can happen in minutes with the right software. Automation pulls data directly from banks, credit card processors, and other sources, eliminating manual downloading and data entry. The system matches transactions automatically based on rules you configure, flagging only exceptions that require human review. This frees your finance team to focus on investigating discrepancies and analyzing financial data rather than performing repetitive data comparison tasks.
- Error reduction is critical for maintaining accurate financial records. Manual reconciliation is prone to mistakes—transposed numbers, skipped lines, incorrect formulas, or simple fatigue when reviewing hundreds of transactions. Automated systems apply consistent matching logic to every transaction, dramatically reducing the risk of human error. When the software flags a discrepancy, you can trust it's a genuine issue rather than wondering if you missed something during manual review.
- Better audit trails emerge naturally from automated reconciliation processes. The software documents who performed the reconciliation, when it was completed, what adjustments were made, and who approved the final results. This creates a complete, timestamped record that satisfies auditor requirements and regulatory standards. Many automation platforms also maintain version history, allowing you to see how reconciliations evolved if questions arise later.
- Continuous reconciliation becomes possible with automation, moving beyond the traditional monthly cycle. Rather than waiting until month-end to discover issues, automated systems can reconcile daily or even in real-time. This dramatically reduces the window for fraud, catches errors while they're fresh and easier to investigate, and eliminates the month-end reconciliation crunch that strains finance teams.
- Real-time alerts and reporting give you instant visibility into your financial position. Automated reconciliation tools can notify your team immediately when discrepancies exceed certain thresholds, when unusual transaction patterns emerge, or when reconciliations aren't completed on schedule. Dashboards show reconciliation status across all accounts at a glance, making it easy for management to monitor financial controls without requesting manual status reports.
When Manual Still Makes Sense
Despite automation's advantages, manual reconciliation remains appropriate in certain scenarios.
- Small businesses with low transaction volumes may find manual reconciliation perfectly adequate. If you're processing 50 transactions per month, spending time and money implementing automation software may not provide sufficient return on investment. A simple Excel spreadsheet and a few hours of work might serve your needs effectively.
- Quick one-off reconciliations for special purposes often don't warrant automation setup. If you need to reconcile a rarely-used account, investigate a specific issue, or perform a special analysis, manual methods can be faster than configuring automation rules for a task you'll only do once.
- Cost considerations matter, especially for businesses with tight budgets. While automation delivers long-term savings through reduced labor and fewer errors, the upfront investment in software licenses, implementation, and training can be prohibitive for some organizations. In these cases, manual reconciliation may be the practical choice until growth justifies the automation investment.
The reality is that most growing businesses eventually reach a tipping point where manual reconciliation becomes unsustainable. Increased transaction volumes, multiple bank accounts, complex operations, and heightened compliance requirements all push organizations toward automation. The key is recognizing when you've reached that point and making the transition before manual processes become a bottleneck that limits your business growth.
Best Practices for Effective Reconciliation
Implementing strong reconciliation best practices transforms this essential task from a compliance requirement into a strategic advantage. Whether you're performing bank reconciliation, vendor reconciliation, or general ledger reconciliation, following these proven practices ensures accuracy, efficiency, and robust financial controls.
1. Reconcile Frequently
Don't wait until month-end to discover discrepancies. Frequent reconciliation—weekly for high-volume accounts or monthly for others—catches errors while they're still fresh and easy to investigate. More frequent reconciliation also reduces the volume of transactions you need to review at one time, making the process less overwhelming and more accurate.
For critical accounts like your primary operating bank account, consider daily reconciliation to maintain real-time visibility and catch fraud immediately.
2. Standardize Your Process
Create documented, repeatable reconciliation procedures that everyone on your team follows consistently. Standardization should cover which documents to gather, what matching criteria to use, how to investigate discrepancies, what documentation to maintain, and approval requirements.
When every reconciliation follows the same process, you reduce errors, make training easier, and ensure nothing gets skipped. Templates and checklists help enforce standardization—many businesses create reconciliation templates in Excel or their accounting software that guide preparers through each required step.
3. Keep Clear Documentation
Document everything related to your reconciliation process. Save all source documents like bank statements, invoices, and receipts. Record explanations for every discrepancy, even timing differences that seem obvious. Maintain a complete audit trail showing who prepared the reconciliation, who reviewed it, when it was completed, and what adjustments were made.
This documentation proves essential during audits, helps train new staff, and protects your business if questions arise about past reconciliations. Most importantly, clear documentation demonstrates to regulators and auditors that your internal controls are functioning effectively.
4. Assign Roles and Responsibilities
Clearly define who is responsible for each aspect of the reconciliation process. Typically, one person prepares the reconciliation while a different person reviews and approves it—this segregation of duties is a fundamental internal control. Document these assignments so everyone knows their responsibilities and deadlines.
Consider rotating reconciliation duties periodically to prevent complacency and reduce fraud risk. When multiple people understand the reconciliation process, you also avoid disruptions when someone is out sick or leaves the company.
5. Review & Approve All Reconciliations
Never allow a reconciliation to be finalized without independent review. The person who prepared the reconciliation shouldn't be the one approving it—fresh eyes catch mistakes the original preparer might miss.
Reviewers should verify that all reconciling items are properly explained, adjustments are supported by documentation, ending balances match correctly, and the reconciliation was completed on time. The reviewer's sign-off creates accountability and provides assurance that reconciliation processes are working as intended.
6. Audit Your Process Periodically
Regularly evaluate your reconciliation procedures to identify weaknesses and opportunities for improvement. Conduct internal audits quarterly or annually to ensure policies are being followed, identify recurring issues that might indicate process problems, verify that documentation standards are being met, and assess whether your current process still fits your business needs.
As your business grows and changes, your reconciliation process should evolve too. What worked when you had 100 monthly transactions may not scale when you reach 10,000.
7. Use Automation Where Feasible
Leverage technology to make reconciliation more efficient and accurate. Even partial automation—like using bank feeds to import transactions automatically—can save significant time and reduce errors. Reconciliation software can match transactions automatically based on rules you configure, flag exceptions for human review, maintain complete audit trails, and generate reconciliation reports instantly.
Start by automating your highest-volume or most time-consuming reconciliations, then expand automation as you see results. The goal isn't to eliminate human involvement entirely but to let technology handle repetitive matching while your team focuses on investigating discrepancies and strengthening controls.
Final Thoughts on Improving Reconciliation Processes
Reconciliation in accounting is the foundation of financial accuracy, stakeholder trust, and regulatory compliance. Regular account reconciliation catches errors early, prevents fraud, and ensures your financial data supports confident decision-making.
For modern finance teams, automation has become essential. Manual reconciliation processes can't keep pace with today's transaction volumes and real-time reporting demands. Automation eliminates repetitive tasks, enables continuous reconciliation, delivers instant alerts for discrepancies, and maintains comprehensive audit trails that simplify compliance.
The most successful organizations view reconciliation as a strategic capability, not an administrative burden. By implementing best practices and leveraging automation technology, your team can shift from reactive error-catching to proactive financial management.
Ready to automate your reconciliation process? Discover how Solvexia can help your team save time and stay audit-ready.
FAQ
Intelligent reconciliation solution
Intelligent rebate management solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent Financial Automation Solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent regulatory reporting solution
Free up time and reduce errors
Recommended for you

Request a Demo
Book a 30-minute call to see how our intelligent software can give you more insights and control over your data and reporting.

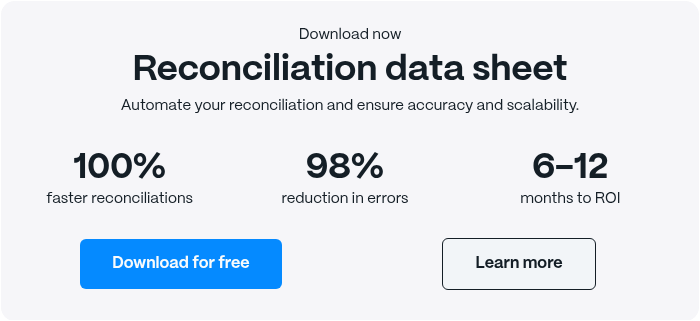
Reconciliation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how to automate your reconciliations for increased accuracy, speed and control.

Regulatory Reporting Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can prepare, validate and submit regulatory returns 10x faster with automation.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Rebate Management Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can manage complex vendor and customer rebates and commission reporting at scale.

Top 10 Automation Challenges for CFOs
Learn how you can avoid and overcome the biggest challenges facing CFOs who want to automate.
.svg)