Everything You Need to Know About EMIR Reporting: A Complete Guide

Regulatory compliance has become a cornerstone of responsible business operations. Among the myriad of regulations, the European Market Infrastructure Regulation (EMIR) stands out as a critical framework for enhancing transparency and reducing systemic risk in the derivatives market. For financial institutions and corporations engaged in derivative trading, understanding and complying with EMIR reporting requirements, including the latest regulatory guidance on derivatives reporting, is not just a legal obligation—it’s a fundamental aspect of sound risk management and operational efficiency.
Since Brexit, UK EMIR has diverged from EU EMIR, leading to separate reporting standards and deadlines. While both frameworks share similar goals, businesses operating across both regions need to be aware of the specific compliance requirements in each jurisdiction. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of EMIR reporting, offering a roadmap for both newcomers and experienced professionals navigating this regulatory terrain.
From the basic definition and scope of EMIR to the nuanced changes introduced by EMIR Refit, we’ll explore who needs to comply, what needs to be reported, and how to streamline the reporting process. Whether you’re a financial counterparty grappling with daily reporting obligations or a non-financial entity seeking to understand your responsibilities, this guide aims to demystify EMIR reporting and equip you with the knowledge to ensure compliance confidently and efficiently.
Coming Up
What is EMIR Reporting?
EMIR Reporting, or reporting under the European Market Infrastructure Regulation (EMIR), is a crucial component of the European Union’s financial regulatory framework. Introduced in 2012, EMIR aims to enhance transparency in the derivatives markets and reduce systemic risk in the financial system.
At its core, EMIR Reporting requires detailed information about each derivative transaction to be reported to authorized Trade Repositories. This reporting obligation applies to both over-the-counter (OTC) derivatives and exchange-traded derivatives, covering a wide range of financial instruments including options, futures, swaps, and forwards.
Key Features of EMIR Reporting
1. Goal of Systemic Risk Reduction:
The primary objective of EMIR Reporting is to mitigate systemic risk in the financial markets. By mandating comprehensive reporting of derivatives transactions, regulators can better monitor market trends, identify potential risks, and take proactive measures to maintain financial stability. Timely and complete reporting is crucial to meet regulatory requirements under the UK's EMIR legislation, ensuring that entities submit accurate reports on time and manage any errors or omissions effectively.
2. Scope of Affected Entities: EMIR Reporting casts a wide net, affecting various participants in the financial ecosystem:
- Financial Counterparties (FCs): This includes banks, investment firms, insurance companies, and other regulated financial institutions.
- Non-Financial Counterparties (NFCs): Companies that use derivatives for hedging or investment purposes, such as energy companies, airlines, or large manufacturers.
- Central Counterparties (CCPs): Entities that act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers in financial markets.
- Trade Repositories: Organizations authorized to collect and maintain records of derivative transactions.
Both EU and non-EU entities can be subject to EMIR reporting obligations if they engage in derivatives transactions that have a connection to the EU market.
By establishing this comprehensive reporting framework, EMIR aims to create a more transparent and stable financial environment, allowing regulators to effectively monitor and manage risks associated with derivative trading.
Who Needs to Comply with EMIR Reporting?
EMIR reporting requirements cast a wide net across the financial landscape, affecting a diverse range of entities engaged in derivative transactions. The reporting regime under both UK and EU EMIR regulations outlines specific requirements and frameworks that govern the reporting of financial instruments. Understanding who needs to comply is crucial for organizations operating within or in connection with the financial markets of the European Union or the United Kingdom.
Since Brexit, there are now two distinct regulatory regimes: UK EMIR and EU EMIR. While both share the same fundamental goals of transparency and risk mitigation, companies must be aware of the specific requirements of each regime. For example, the implementation timelines and certain reporting fields differ between UK EMIR and EU EMIR, necessitating separate compliance strategies for organizations operating in both regions.
Financial and Non-Financial Counterparties
EMIR reporting obligations apply to two main categories of entities: Financial Counterparties (FCs) and Non-Financial Counterparties (NFCs). Let’s break down each category:
Financial Counterparties (FCs):
- Banks and credit institutions
- Investment firms
- Insurance and reinsurance companies
- Undertakings for Collective Investment in Transferable Securities (UCITS) and their management companies
- Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs) managed by Alternative Investment Fund Managers (AIFMs)
- Institutions for occupational retirement provision (IORPs)
FCs are subject to EMIR reporting requirements for all their derivative contracts, regardless of the purpose or volume of these transactions. In both the UK and the EU, FCs must adhere to the specific reporting rules and deadlines set by the respective regulatory authorities (FCA for the UK and ESMA for the EU).
Non-Financial Counterparties (NFCs):
- Any entity established within the EU or UK that is not classified as a Financial Counterparty
- Examples include energy companies, airlines, manufacturing firms, and technology companies
NFCs are further divided into two subcategories:
- NFC+: NFCs whose trading volume in OTC derivatives exceeds specific thresholds set by EMIR. These entities have reporting obligations similar to FCs.
- NFC-: NFCs whose trading volume remains below the EMIR thresholds. While they still have reporting obligations, these are generally less extensive than those for NFC+ entities.
It's important to note that EMIR reporting obligations can extend to entities outside the UK and EU under certain circumstances, such as:
- Non-EU or non-UK entities trading with EU or UK counterparties
- EU or UK branches of non-EU or non-UK entities
- Non-EU or non-UK subsidiaries of EU or UK parent companies, in some cases
The responsibility for reporting typically falls on both counterparties involved in a transaction. However, there are provisions for delegated reporting, where one party can report on behalf of both, subject to specific agreements and conditions.
Understanding your entity’s classification and the resulting reporting obligations is crucial for compliance with EMIR. The classification can impact not only the reporting requirements but also other EMIR obligations, such as clearing and risk mitigation techniques. Additionally, companies operating across both the UK and EU must navigate the nuanced differences between UK EMIR and EU EMIR to ensure full compliance in both jurisdictions.
EMIR Reporting Requirements for Derivative Contracts
EMIR imposes comprehensive reporting obligations on entities engaged in any derivative contract, requiring them to report the specifics of each contract they have entered into, modified, or terminated. Understanding these requirements is crucial for ensuring compliance and avoiding potential penalties.
Mandatory Reporting and Trade Repositories
EMIR mandates that all derivative contracts must be reported to authorized Trade Repositories (TRs). Here are the key aspects of this requirement:
What needs to be reported:
- All derivative contracts (both OTC and exchange-traded)
- New contracts
- Modifications or terminations of existing contracts
- Valuation updates
- Collateral information
Information to be included in reports:
- Counterparty details (such as LEI codes)
- Contract type and characteristics
- Transaction details (including price, notional amount, and currency)
- Clearing information
- Valuation and collateral data
- Execution timestamp and venue
Authorized Trade Repositories:
- Reports must be submitted to ESMA-registered Trade Repositories
- As of 2023, there are several authorized TRs, including DTCC, UnaVista, and REGIS-TR
Reporting responsibility:
- Both counterparties are responsible for reporting
- Options for delegated reporting exist, but ultimate responsibility remains with the counterparties
Unique Transaction Identifier (UTI):
- Each reported transaction must have a UTI
- Counterparties must agree on who generates the UTI
Entities must also rectify any identified errors or omissions and submit the appropriate errors and omissions form to the relevant authority, especially when substantial errors necessitate a remediation plan.
Reporting Deadlines
EMIR sets strict timelines for reporting derivative transactions:
T+1 reporting:
- New contracts, modifications, and terminations must be reported by the end of the working day following the event (T+1)
Valuation and collateral updates:
- For Financial Counterparties and NFC+:
- Daily valuation updates for centrally cleared trades
- Daily collateral updates for uncleared trades
- NFC- entities are exempt from daily valuation and collateral reporting
Error correction:
- Any identified errors or omissions in reported data must be corrected without undue delay
- Entities must ensure all outstanding derivative reports comply with new regulatory requirements by the end of the transition period
Reconciliation:
- Counterparties must ensure their reported data matches, reconciling any discrepancies promptly
Record keeping:
- All reported information must be kept for at least 5 years after the termination of the contract
Understanding and adhering to these reporting requirements and deadlines is essential for maintaining compliance with EMIR. Entities subject to EMIR should have robust systems and processes in place to capture, validate, and report the required information within the specified timeframes.
EMIR Refit: What’s New?
The EMIR Refit (Regulatory Fitness and Performance program) is a significant update to the original EMIR regulation, designed to reduce the regulatory burden on smaller entities while maintaining the overarching goals of EMIR—transparency and risk mitigation in the derivatives market. Implemented in 2019, the EMIR Refit introduced several important changes, with new reporting requirements taking effect on April 29, 2024, in the EU and September 30, 2024, in the UK.
Key Updates and Changes
- Simplified Reporting for Smaller Entities:
- Exemption for Small Financial Counterparties (SFCs): Small Financial Counterparties are now exempt from the clearing obligation if their average position remains below the thresholds set by EMIR. This change aims to alleviate the regulatory burden on entities that pose less systemic risk.
- Refined Reporting Obligations:
- Single-Sided Reporting: Financial Counterparties (FCs) now assume responsibility for reporting on behalf of both counterparties in transactions involving Non-Financial Counterparties below the clearing threshold (NFC-). This shift reduces the reporting burden on smaller non-financial entities.
- Re-reporting of Outstanding Contracts: All outstanding contracts must be updated to comply with the new standards within 180 days of the go-live dates (April 29, 2024, for the EU, and September 30, 2024, for the UK). This involves re-reporting existing trades with additional or expanded details, including new fields under the ISO 20022 XML data format.
- Risk Mitigation Techniques:
- Clearing Thresholds: The calculation of positions against clearing thresholds now occurs annually instead of every 30 days. This reduces the frequency of assessments for Non-Financial Counterparties (NFCs) and ensures that clearing obligations only apply when thresholds are exceeded in specific asset classes.
- Frontloading Requirement Removed: The obligation to clear contracts entered into before the clearing obligation takes effect (frontloading) has been eliminated. This simplifies compliance for entities engaging in derivatives trading.
- Enhanced Data Quality and Reporting Standards:
- ISO 20022 XML Data Format: The adoption of this new messaging standard facilitates improved data exchange between market participants and regulatory authorities, enhancing the accuracy and consistency of reporting.
- Increased Reporting Fields: The number of reporting fields has expanded from 129 to 204, including new fields related to notional schedules, spreads, and options. This expansion aims to provide regulators with deeper insights into market activities.
- Intragroup Transaction Exemptions: Reporting requirements for intragroup transactions where one counterparty is an NFC have been waived under specific conditions. This change further reduces the compliance burden on smaller entities.
Impact on Smaller Entities
The EMIR Refit introduces a more nuanced approach to financial regulation by acknowledging the diverse landscape of market participants. Smaller Financial Counterparties and Non-Financial Counterparties below the clearing threshold (NFC-) benefit from reduced reporting obligations and exemptions from certain requirements. These changes reflect a proportional approach, ensuring that entities posing less systemic risk face fewer regulatory hurdles while maintaining overall market transparency and stability.
How to Simplify EMIR Reporting
Complying with EMIR reporting requirements can be complex and resource-intensive, especially for smaller entities or those new to the regulation. However, there are several strategies and tools available to simplify the process and ensure accurate, timely reporting.
1. Implement Robust Data Management Systems:
- Invest in systems that can automatically capture and organize trade data.
- Ensure your systems can handle all required data fields and formats specified by EMIR. Additionally, adhere to UK EMIR validation rules to ensure accurate and efficient reporting.
2. Utilize Automated Reporting Tools:
- Consider adopting specialized EMIR reporting software that can:
- Automatically extract relevant data from your trading systems.
- Validate data against EMIR requirements.
- Generate reports in the correct format for submission to Trade Repositories.
3. Establish Clear Internal Processes:
- Develop step-by-step procedures for collecting, validating, and submitting reports.
- Assign clear responsibilities to team members for each stage of the reporting process.
4. Conduct Regular Training:
- Ensure all relevant staff are up-to-date with EMIR requirements and your internal reporting procedures.
- Provide refresher training when regulations change.
5. Perform Regular Reconciliations:
- Implement a process to regularly reconcile your reported data with your counterparties.
- Address any discrepancies promptly to maintain accurate reporting.
6. Stay Informed About Regulatory Changes:
- Subscribe to regulatory updates from ESMA and your chosen Trade Repository.
- Consider joining industry associations that provide updates and guidance on EMIR reporting.
7. Leverage APIs:
- If available, use APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) provided by Trade Repositories to streamline the submission process.
Delegated Reporting Solutions
One of the most effective ways to simplify EMIR reporting is through delegated reporting. This approach can be particularly beneficial for smaller entities or those with limited resources.
1. Understanding Delegated Reporting:
- Delegated reporting allows one counterparty (typically the more sophisticated party) to report on behalf of both parties to a trade.
- While reporting can be delegated, the legal responsibility for ensuring accurate and timely reporting remains with both parties.
2. Benefits of Delegated Reporting:
- Reduces the operational burden on smaller entities.
- Leverages the expertise and systems of larger, more experienced counterparties.
- Can improve reporting consistency and reduce errors.
3. How to Implement Delegated Reporting:
- Identify potential reporting delegates (e.g., your bank, broker, or a specialized third-party provider).
- Negotiate and establish a clear delegated reporting agreement, outlining:
- Scope of delegated activities
- Data sharing procedures
- Responsibilities for data accuracy and timeliness
- Processes for addressing errors or omissions
4. Choosing a Delegated Reporting Provider:
- Consider providers with:
- Robust reporting infrastructure
- Expertise in EMIR requirements
- Strong track record in regulatory compliance
- Clear communication channels and support services
5. Maintaining Oversight:
- Even with delegated reporting, implement processes to:
- Regularly review reported data for accuracy
- Maintain open communication with your reporting delegate
- Stay informed about regulatory changes that might affect your reporting obligations
6. Third-Party Reporting Services:
- Consider specialized third-party providers offering end-to-end EMIR reporting solutions.
- These services often include:
- Data extraction and normalization
- Report generation and submission
- Reconciliation services
- Regulatory updates and compliance guidance
- Reconciliation statistics report files, which include both updated and non-updated contracts due to the relaxed XML schemas for reporting derivative trades during the transition period from 30 September 2024 to 31 March 2025.
By leveraging these strategies and solutions, entities can significantly simplify their EMIR reporting processes, reduce the risk of non-compliance, and free up resources to focus on core business activities. Remember, while tools and services can greatly assist in the reporting process, it’s crucial to maintain an understanding of your obligations and oversight of your reporting activities.
Wrapping Up
As we've explored throughout this guide, EMIR reporting is a complex but crucial aspect of operating in the European derivatives market. From understanding the fundamental objectives of EMIR to navigating the streamlined processes introduced by EMIR Refit, compliance requires a thorough understanding of your obligations and a strategic approach to implementation.
Key takeaways include:
- The broad scope of EMIR, affecting both financial and non-financial counterparties
- The critical role of accurate and timely reporting in mitigating systemic risk
- The importance of understanding your entity's classification and resulting obligations
- The opportunities for simplification through delegated reporting and automated solutions
- The ongoing need to stay informed about regulatory changes and maintain robust compliance processes
While EMIR reporting may seem daunting, particularly for smaller entities, the regulatory landscape is evolving to balance effective oversight with practical implementation. By leveraging the strategies and solutions discussed in this guide, organizations can not only achieve compliance but also gain valuable insights into their derivatives activities.
Remember, EMIR reporting is not just about ticking regulatory boxes—it's an opportunity to enhance your risk management practices, improve operational efficiency, and contribute to a more transparent and stable financial market. As the financial world continues to evolve, staying informed and adaptable in your approach to EMIR reporting will be key to navigating the complexities of regulatory compliance successfully. Download our data sheet to see how you can streamline your EMIR reporting using Solvexia.
FAQ
Intelligent reconciliation solution
Intelligent rebate management solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent Financial Automation Solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent regulatory reporting solution
Free up time and reduce errors
Recommended for you

Request a Demo
Book a 30-minute call to see how our intelligent software can give you more insights and control over your data and reporting.

Reconciliation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how to automate your reconciliations for increased accuracy, speed and control.

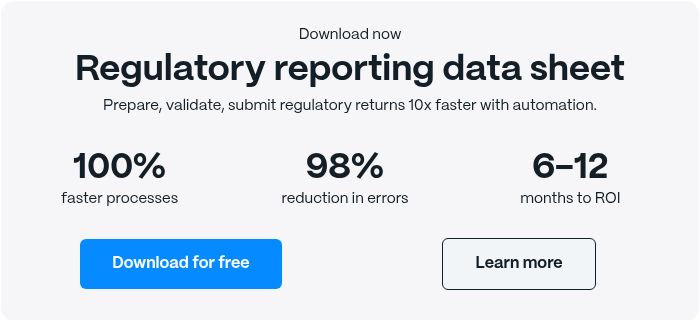
Regulatory Reporting Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can prepare, validate and submit regulatory returns 10x faster with automation.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Rebate Management Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can manage complex vendor and customer rebates and commission reporting at scale.

Top 10 Automation Challenges for CFOs
Learn how you can avoid and overcome the biggest challenges facing CFOs who want to automate.
.svg)