Mastering Audit Reconciliation: Processes, Challenges, and Solutions

Managing accurate financial records is a challenge—one that audit reconciliation can solve. As a cornerstone of financial accuracy, audit reconciliation provides a systematic process to verify and validate financial records by comparing two or more sets of data to ensure agreement. This critical process, especially when enhanced through financial automation, involves matching transactions across different financial documents and systems to identify discrepancies, errors, or suspicious activities.
Manual reconciliation processes often introduce significant challenges:
- Time-intensive data entry and cross-checking
- Higher risk of human error in transaction matching
- Delayed detection of discrepancies
- Limited visibility into reconciliation status
- Difficulty maintaining consistent documentation
With effective audit reconciliation, organizations can strengthen their control frameworks, identify and fix issues, enhance internal controls, improve financial reporting accuracy, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Coming Up
Understanding Audit Reconciliation
Audit reconciliation is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of financial records. It involves comparing financial data across sources—like bank statements, general ledgers, and accounting systems—to identify and resolve discrepancies. This process is crucial for maintaining data integrity, preventing errors or fraudulent transactions, and ensuring compliance with accounting principles and regulations.
By reconciling transactions systematically, organizations can detect inconsistencies early, enhancing the accuracy of financial reporting. Audit reconciliation not only fortifies internal controls but also acts as a safeguard, ensuring recorded transactions are accurate and legitimate.
The Importance of Audit Reconciliation
Audit reconciliation is crucial for several reasons:
- Ensures Accuracy: By meticulously comparing financial records, audit reconciliation helps identify and correct errors, ensuring that financial statements are accurate and reliable. This accuracy is vital for maintaining trust with stakeholders and making informed business decisions.
- Prevents Fraudulent Transactions: Regular reconciliation can detect and prevent fraudulent transactions, such as unauthorized withdrawals or deposits. By comparing data from different sources, organizations can quickly spot discrepancies that may indicate fraudulent activity.
- Maintains Compliance: Audit reconciliation ensures that financial records comply with accounting principles and regulations, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties. This compliance is essential for avoiding legal issues and maintaining a good standing with regulatory bodies.
- Supports Financial Decision-Making: Accurate and reliable financial records are the foundation of informed financial decision-making. By ensuring that all transactions are correctly recorded and reconciled, organizations can make better strategic decisions that drive business success.
The Role of Bank Reconciliation in Internal Controls
Effective internal controls rely heavily on regular reconciliation processes. When integrated into an organization's financial workflow, audit reconciliation serves as a crucial detective control, helping identify errors, fraud, and discrepancies before they impact financial statements.
Bank reconciliation audit procedures play a particularly vital role, acting as the first line of defense in:
- Detecting unauthorized transactions
- Identifying missing deposits or payments
- Preventing cash flow discrepancies
- Ensuring accurate financial reporting
- Supporting regulatory compliance
Beyond basic transaction matching, audit reconciliation strengthens internal controls by creating documented evidence of review, establishing clear accountability, and maintaining a verifiable audit trail. This systematic approach helps organizations meet both internal governance requirements and external regulatory standards.
How to Conduct an Effective Audit Reconciliation
Step-by-Step Guide
1. Document Collection
- Gather bank statements and transaction records
- Access general ledger entries and account details
- Pull relevant reconciliation reports from previous periods
- Collect supporting documentation for unusual items
2. Review and Analysis
- Compare opening balances with prior reconciliations
- Match transactions between statements and bank accounts ledgers
- Flag unmatched items for investigation
- Document reconciling items clearly
3. Resolution Process
- Investigate discrepancies systematically
- Track timing differences and outstanding items
- Make necessary adjusting entries
- Document all resolution steps taken
Benefits of Automation in Reconciliation Audits
Modern reconciliation software transforms the traditional audit process by automating key tasks and enhancing accuracy. Advanced reconciliation tools such as Solvexia offer significant advantages:
- Automatic transaction matching using customizable rules
- Real-time exception identification and flagging
- Standardized workflows for consistent processing
- Secure audit trails with detailed activity logs
- Automated report generation for stakeholder review
This automation reduces manual effort while improving accuracy, allowing finance teams to focus on investigating discrepancies rather than routine matching tasks.
Solvexia's reconciliation platform exemplifies these benefits by providing end-to-end automation capabilities that have helped organizations reduce audit preparation time by up to 80% and identify potential issues before they impact financial statements.
Bank Reconciliation Process
The bank reconciliation process involves several key steps to ensure that the financial records are accurate and up-to-date:
- Gather Financial Data: Collect all relevant financial data, including bank statements, general ledgers, and accounting system data. This comprehensive data collection is the first step in identifying any discrepancies.
- Compare Financial Data: Carefully compare the financial data from different sources to identify any discrepancies. This involves matching transactions recorded in the bank statement with those in the general ledger and accounting system.
- Identify and Resolve Discrepancies: Investigate any discrepancies found during the comparison process. This may involve identifying errors or fraudulent transactions and taking the necessary steps to resolve them.
- Verify Ending Balance: Ensure that the ending balance on the bank statement matches the book balance in the general ledger. This verification step is crucial for confirming that all transactions have been accurately recorded.
- Document Reconciliation: Document the entire reconciliation process, including any discrepancies found and the steps taken to resolve them. This documentation provides a clear audit trail and supports future reconciliation efforts.
Three-Way Reconciliation
Three-way reconciliation is a comprehensive process that involves comparing and matching financial data from three distinct sources:
- Bank Statement: The bank statement provides a detailed record of all transactions and the ending balance. It serves as an external verification of the transactions recorded by the organization.
- General Ledger: The general ledger contains a record of all financial transactions and the book balance. It is the primary source of financial data within the organization.
- Accounting System: The accounting system provides a record of transactions and the system balance. It integrates data from various sources and ensures that all financial records are up-to-date.
By comparing and matching financial data from these three sources, three-way reconciliation ensures that financial records are accurate, reliable, and compliant with accounting principles and regulations. This process helps organizations maintain robust financial controls and supports the integrity of their financial reporting.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Reconciliation Audits
Reconciliation audits often face several persistent challenges that can impact accuracy and efficiency. Understanding these obstacles and implementing appropriate solutions is crucial for maintaining effective financial controls.
Key Challenges
1. Manual Data Processing
- Hours spent on data entry and cross-checking
- Difficulty handling large transaction volumes
- Inconsistent formatting across data sources
- Risk of missing critical transactions
2. Spreadsheet Limitations
- Version control issues
- Formula errors and broken links
- Limited collaboration capabilities
- Inadequate audit trails
- Security and access control concerns
3. Error Susceptibility
- Fatigue-induced mistakes during repetitive tasks
- Transposition errors in manual entry
- Inconsistent reconciliation procedures
- Delayed error detection
Modern Solutions
Financial automation offers effective solutions to these traditional challenges:
1. Automated Data Processing
- Direct integration with banking and accounting systems
- Automatic transaction matching and categorization
- Built-in validation rules and error checks
- Real-time processing and updates
2. Enhanced Control and Visibility
- Centralized platform for all reconciliation activities
- Standardized workflows and procedures
- Clear audit trails and change history
- Role-based access controls
3. Improved Accuracy and Speed
- Elimination of manual data entry
- Consistent application of matching rules
- Immediate flagging of discrepancies
- Faster resolution of exceptions
By implementing these solutions, organizations can transform their reconciliation process from a time-consuming, error-prone task into a streamlined, reliable operation that supports stronger financial controls.
Best Practices for Successful Reconciliation Audits
Implementing robust reconciliation practices is essential for maintaining financial accuracy and meeting compliance requirements. Here are key best practices that organizations should follow:
Establish Regular Review Cycles
- Perform daily reconciliation for high-volume accounts
- Complete monthly reconciliations by the 10th of following month
- Conduct comprehensive quarterly reviews
- Schedule annual audits to verify systematic compliance
- Set clear deadlines and accountability for each cycle
Supporting Documentation and Audit Trails
Maintain detailed records of all reconciliation activities:
- Document all reconciling items with explanations
- Keep supporting evidence for adjustments
- Record review and approval signatures
- Store historical reconciliation reports
- Maintain systematic documentation of exceptions
Quality Control Measures
1. Segregation of Duties
- Separate preparers from reviewers
- Rotate reconciliation responsibilities
- Establish clear approval hierarchies
- Implement multiple levels of review for critical accounts
2. Standardized Procedures
- Create detailed reconciliation templates
- Develop clear escalation protocols
- Establish consistent naming conventions
- Define standard resolution procedures
3. Regular Monitoring
- Track reconciliation completion rates
- Monitor aging of unreconciled items
- Review patterns in reconciling items
- Assess staff performance and efficiency
Following these best practices ensures not only compliance with regulatory requirements but also builds a foundation for efficient, accurate financial operations.
Wrap Up
Effective audit reconciliation is fundamental to maintaining financial accuracy and compliance. By implementing robust reconciliation processes, leveraging automation tools, and following established best practices, organizations can significantly improve their financial control and operational efficiency.
Key takeaways for mastering audit reconciliation:
- Regular reconciliation cycles are essential for maintaining accuracy
- Automation reduces manual effort while improving precision
- Proper documentation and audit trails ensure compliance
- Standardized procedures strengthen internal controls
Ready to optimize your audit reconciliation? Request a demo to learn how Solvexia’s automation tool can transform your financial workflows today.
FAQ
Intelligent reconciliation solution
Intelligent rebate management solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent Financial Automation Solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent regulatory reporting solution
Free up time and reduce errors
Recommended for you

Request a Demo
Book a 30-minute call to see how our intelligent software can give you more insights and control over your data and reporting.

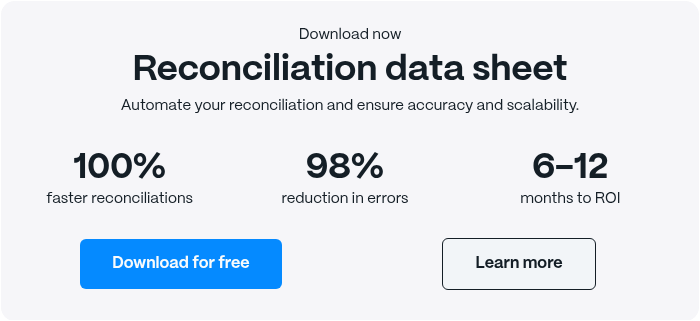
Reconciliation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how to automate your reconciliations for increased accuracy, speed and control.

Regulatory Reporting Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can prepare, validate and submit regulatory returns 10x faster with automation.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Rebate Management Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can manage complex vendor and customer rebates and commission reporting at scale.

Top 10 Automation Challenges for CFOs
Learn how you can avoid and overcome the biggest challenges facing CFOs who want to automate.
.svg)