Accounts Receivable Reconciliation: Steps & Best Practices

There’s no month-end close process completed without the completion of accounts receivable (AR) reconciliation. This highly important practice is needed to ensure that invoices are properly paid and the business gets what it is owed. Automation has significantly improved the AR process by increasing efficiency, reducing errors, and streamlining steps such as invoicing, reconciliation, and cash collection.
To help manage the different types of general ledger reconciliation, companies are using automation software to streamline and optimize the month-end close checklist. Maintaining accurate and organized accounting records is essential for effective automation and successful accounts receivable reconciliation.
We’re going to share some useful tips and best practices to introduce to your AR reconciliation process to ensure reliable financial reporting.
Coming Up
What is Accounts Receivable Reconciliation?
Why is AR Reconciliation Important?
When & How Often Should You Reconcile AR?
Common Accounts Receivable Reconciliation Errors
Step-by-Step: How to Reconcile Accounts Receivable
Accounts Receivable Aging: Monitoring Overdue Balances
Preventing Bad Debts Through Effective Reconciliation
How Automation Enhances AR Reconciliation
Industry Examples of AR Reconciliation
Final Thoughts: Streamlining AR Reconciliation for Your Business
What is Accounts Receivable Reconciliation?
Accounts receivable reconciliation is the critical accounting process of cross-checking your customer’s unpaid invoices against the accounts receivable balance recorded in your general ledger. Simply put, it’s verifying that what your customers actually owe matches exactly what your books say they owe. AR reconciliation works as a step-by-step process: it involves comparing the accounts receivable balance with customer invoices, investigating any discrepancies, and recording necessary adjustments to ensure your financial records are accurate.
This verification process involves several key steps, such as reviewing balances, matching transactions, and resolving inconsistencies. It ensures your financial records accurately reflect reality—helping to identify discrepancies and prevent costly errors that could lead to cash flow miscalculations, incorrect financial statements, or poor business decisions based on faulty data.
General Ledger vs. AR Ledger
Understanding the difference between these two ledgers is essential for effective reconciliation:
General Ledger
- Your company’s master accounting record using double-entry bookkeeping
- Tracks both credits and debits that balance each other out across all accounts
- Contains the summary balance of total accounts receivable
- Shows the “big picture” of what customers owe your business overall
- It is important to reconcile the general ledger balance with the receivable ledger and open invoices to ensure that all unpaid customer billings are accurately reflected, especially during month-end close and financial reporting.
AR Ledger (Subsidiary Ledger)
- A detailed, line-by-line record of each individual customer’s outstanding bills (also known as the receivable ledger)
- Shows specific invoices, payment dates, and amounts for every customer account
- Provides the granular detail behind the general ledger’s summary balance
- Contains information like invoice numbers, due dates, and payment history
In a perfectly managed system, the total of all individual customer balances—representing unpaid customer billings or open invoices—in your AR ledger (receivable ledger) should exactly equal the general ledger balance.
Why Accuracy Matters
When these two ledgers don’t align, it signals potential problems that can impact your business:
- Cash flow forecasting errors: Thinking you have more money coming in than you actually do
- Customer relationship issues: Billing disputes from inaccurate records
- Compliance problems: Inaccurate financial statements for tax reporting or audits
- Operational inefficiencies: Time wasted chasing payments that were already made
- Strategic missteps: Business decisions based on incorrect financial data
- Potential errors: Issues such as duplicate entries, missed payments, and incorrect postings
Reconciliation processes catch these discrepancies before they compound into larger financial problems, helping to reduce human error and potential errors, and ensuring your accounts receivable accurately reflects your true financial position.
By automating reconciliation processes and implementing process improvements, you can reduce manual errors and improve efficiency in AR reconciliation.
Why is AR Reconciliation Important?
AR reconciliation protects your financial health and supports informed business decisions. Here's why it matters:
Financial Accuracy
AR reconciliation ensures your balance sheet accurately reflects what customers owe, preventing costly financial statement errors. During reconciliation, it is important to verify the general ledger figure for accounts receivable to ensure all records are accurate. Regular reconciliation catches problems early:
- Data entry mistakes and duplicate entries
- Unrecorded payments making accounts appear overdue
- Misallocated transactions posted to wrong accounts
- Timing differences between transaction dates and recording dates
- Ensuring the ending balance in the AR ledger matches the general ledger and is properly reflected in financial statements
Bank reconciliation is another important process for verifying financial accuracy and ensuring consistency between internal records and bank statements.
Cash Flow Insights
Accurate AR records enable confident cash flow forecasting and smarter collection strategies:
- Know exactly which customers owe money and when payments are due
- Identify customer payment patterns to optimize credit policies
- Prioritize follow-up with genuinely overdue accounts
- Avoid embarrassing collection calls to customers who already paid
- Regularly monitor incoming payments to ensure they are matched to outstanding invoices
Collecting payments efficiently is crucial for healthy cash flow. Using automation tools can help streamline the process of collecting payments and reconciling incoming payments, reducing errors and saving time.
Compliance & Fraud Prevention
AR reconciliation supports regulatory compliance and acts as a fraud detection control:
- Tax Reporting: Ensures all taxable transactions are properly recorded
- Financial Audits: Provides clean records that reduce audit time and costs
- Fraud Detection: Identifies unauthorized transactions and suspicious patterns
- Customer Relations: Prevents billing disputes and maintains trust through accurate records
When & How Often Should You Reconcile AR?
The frequency of AR reconciliation depends on your business size, transaction volume, and risk tolerance. Here's how to determine the right schedule:
Monthly Reconciliation (Standard Practice)
Most businesses perform AR reconciliation as part of their month-end close process. This timing works well because:
- Aligns with financial statement preparation
- Catches errors before they compound
- Supports accurate monthly cash flow projections
- Meets most compliance and audit requirements
Weekly or Daily Reconciliation (High-Volume Businesses)
Companies with high transaction volumes or critical cash flow needs should consider more frequent reconciliation:
- E-commerce businesses with daily sales
- Service companies with subscription billing
- Businesses with seasonal cash flow patterns
- Companies managing multiple payment processors
Event-Triggered Reconciliation
Beyond regular schedules, perform reconciliation after:
- Major sales events or promotions
- System upgrades or data migrations
- Significant customer acquisitions or losses
- Before important financial decisions or funding rounds
- When investigating customer payment disputes
Annual Minimum
At minimum, perform comprehensive AR reconciliation annually for:
- Year-end financial statement preparation
- Tax reporting requirements
- Annual audit preparation
- Strategic financial planning
The key is consistency—whatever frequency you choose, stick to it and ensure your team has clear procedures and deadlines for completion.
Common Accounts Receivable Reconciliation Errors
Even with careful processes, AR reconciliation challenges are common. Understanding these typical errors helps you spot and resolve them quickly, maintaining accurate financial records.
1. Unapplied Cash
What it is: Payments received from customers but not linked to specific invoices, leaving both cash and invoices appearing in your system incorrectly.
Why it happens:
- Customer payments without invoice references
- Partial payments split across multiple invoices
- Payments received before invoices are generated
- Different payment amounts than invoice totals due to discounts or disputes
Impact: Makes it appear you have more outstanding receivables than reality, skewing cash flow forecasts and collection efforts.
2. Timing Mismatches
What it is: Transactions recorded in different accounting periods, creating temporary discrepancies between your AR ledger and general ledger.
Why it happens:
- Invoices issued near month-end but recorded in the following period
- Payments received in one month but processed in another
- Cut-off differences between sales and accounting teams
- Bank processing delays affecting payment dates
Impact: Distorts monthly financial statements and makes period-over-period comparisons unreliable.
3. Customer Record Errors
What it is: Discrepancies between what your business records show and what customers believe they owe.
Why it happens:
- Invoicing errors or incorrect pricing
- Unrecorded customer returns or exchanges
- Disputed charges not properly documented
- Communication gaps about payment terms or discounts
- Multiple customer locations with different billing arrangements
Impact: Creates collection disputes, damages customer relationships, and delays payment resolution.
4. Data Entry Mistakes
What it is: Human errors in recording transaction amounts, dates, or customer information.
Why it happens:
- Manual data entry in multiple systems
- Transposed numbers (typing 1,234 instead of 1,243)
- Wrong customer accounts selected during entry
- Duplicate invoice or payment entries
- Copy-paste errors between spreadsheets
Impact: Creates false discrepancies that waste time investigating and can lead to incorrect collection actions.
Step-by-Step: How to Reconcile Accounts Receivable
The AR reconciliation process follows a systematic approach that ensures accuracy and completeness. Here's how to execute each step effectively:
1. Data Collection
Gather all necessary documentation for the reconciliation period:
Required Documents:
- Aged accounts receivable report from your AR system
- General ledger account balance for accounts receivable
- Customer invoices and credit memos issued during the period
- Payment receipts and bank deposits
- Any adjustments or write-offs made to customer accounts
Preparation Checklist:
- Ensure all transactions for the period are posted and complete
- Verify cut-off dates are consistent across all reports
- Confirm all bank deposits have been recorded
- Export data from consistent date ranges across all systems
2. Compare Entries
Systematically match your detailed customer records against the general ledger summary:
Matching Process:
- Compare the total AR balance in your general ledger to the sum of all individual customer balances
- Identify any numerical differences between the two totals
- Cross-reference individual customer invoices with recorded receivables
- Check that all payments received match customer account credits
- Verify credit memos and adjustments appear in both systems
Documentation:
- Create a reconciliation worksheet showing both balances
- Note any differences found during the comparison
- Flag items that don't have clear matches between systems
3. Investigate Discrepancies
When balances don't match, investigate systematically to identify root causes:
Common Investigation Steps:
- Review recent journal entries that might affect AR balances
- Check for unposted transactions in either system
- Verify timing differences (payments received but not yet applied)
- Look for duplicate entries or misallocated transactions
- Contact customers for payment confirmation when necessary
- Review bank statements for deposits not yet recorded
Resolution Actions:
- Correct data entry errors found during investigation
- Post any missing journal entries to align the records
- Apply unapplied cash to appropriate customer invoices
- Write off confirmed uncollectible accounts following company policy
4. Adjust and Report
Complete the reconciliation process and document your findings:
Final Adjustments:
- Post correcting journal entries to resolve identified discrepancies
- Update customer account records with accurate balances
- Record any necessary allowances for doubtful accounts
- Ensure both systems now show matching totals
Reporting and Documentation:
- Prepare a reconciliation summary showing opening balance, adjustments, and closing balance
- Document all corrections made and their business justification
- Update customer statements with accurate balances
- Archive reconciliation workpapers for audit and compliance purposes
- Communicate significant findings to management and relevant departments
This systematic approach ensures accuracy while creating an audit trail for future reference. The time invested in thorough reconciliation prevents larger issues and supports confident financial decision-making.
Accounts Receivable Aging: Monitoring Overdue Balances
Accounts receivable aging is an essential part of the accounts receivable reconciliation process, providing businesses with a clear, detailed listing of all outstanding invoices sorted by how long they have remained unpaid. This aging report is a powerful tool for monitoring upcoming or overdue payments, as it categorizes receivables into time buckets—such as current, 30 days overdue, 60 days overdue, and beyond—making it easy to spot which accounts require immediate attention.
By regularly reviewing the accounts receivable aging report, businesses can quickly identify potential bad debts and prioritize their collection efforts. This proactive approach not only helps reduce the risk of uncollectible accounts but also supports accurate financial statements and healthier cash flow. The aging process enables teams to send timely reminders for overdue payments, follow up on discrepancies, and take action before small issues escalate into major problems.
Effective use of accounts receivable aging also strengthens healthy customer relationships. By addressing overdue payments promptly and professionally, businesses can maintain open communication with customers and resolve disputes before they impact the bottom line. Integrating the aging report into your receivable reconciliation process ensures that all outstanding balances are accounted for, discrepancies are resolved quickly, and your financial statements remain accurate.
Preventing Bad Debts Through Effective Reconciliation
Preventing bad debts is a critical goal of the accounts receivable reconciliation process. Bad debts can erode profitability, disrupt cash flow, and undermine the accuracy of your financial records. By implementing thorough reconciliation procedures, businesses can spot potential issues—such as unrecorded payments, duplicate entries, or timing discrepancies—before they develop into uncollectible accounts.
Regularly reconciling accounts receivable with the general ledger and subsidiary sales ledger allows you to detect discrepancies early and take corrective action. This includes investigating unmatched payments, resolving errors in customer accounts, and ensuring all transactions are recorded accurately. Using accounting software to automate the receivable reconciliation process further reduces manual errors and increases efficiency, making it easier to maintain up-to-date financial records.
A strong credit management process also plays a key role in preventing bad debts. This involves routinely reviewing customer accounts, performing credit checks, and setting clear payment terms. By monitoring payment patterns and acting quickly on overdue accounts, businesses can minimize the risk of bad debts and maintain healthy customer relationships.
Ultimately, prioritizing the reconciliation process and leveraging technology to reduce manual errors helps businesses safeguard their cash flow and financial health. Promptly identifying and addressing discrepancies ensures that potential bad debts are managed before they become a problem, supporting accurate financial statements and long-term business success.
How Automation Enhances AR Reconciliation
Modern AR reconciliation software transforms time-consuming manual processes into streamlined, accurate workflows.
Reduce Manual Work & Errors
Automation eliminates data entry mistakes by automatically importing transaction data, removing the risk of typos and duplicate entries. It centralizes data from your CRM, ERP, and banking platforms into one clean format, reducing reconciliation time from days to hours. Standardized workflows prevent key person dependency and free your finance team to focus on strategic analysis rather than cross-checking spreadsheets.
Improve Compliance & Transparency
AR automation maintains complete audit trails with timestamps and user tracking for every transaction, satisfying compliance requirements. When payment disputes arise, automated systems provide definitive proof of invoice delivery and payment status. Real-time reporting enables better cash flow management and eliminates waiting for month-end manual processes.
Integration With Payment Platforms
Modern businesses receive payments through multiple channels including Stripe, PayPal, Amazon Pay, and bank transfers. AR automation consolidates all payment streams into a single view, automatically matches payments to invoices even with incomplete references, and uses predictive analytics to identify customers likely to pay late. Real-time processing eliminates timing mismatches and improves cash flow visibility.
Industry Examples of AR Reconciliation
Every business that issues invoices should be performing AR reconciliation.
Here’s how that looks across industries:
1. Insurance Industry
Insurance companies conduct AR reconciliation to verify that they are receiving the right payments from insurance providers and customers. It’s critical in this industry for financial statements to be right, as well as to properly be able to mitigate risk.
2. Retail Industry
For retailers, customer invoices and payments are issued at a high frequency. AR automation software tracks outstanding balances and purchases to be sure they are paid on time.
3. Financial Services Industry
Financial service providers have to oversee customer transactions, such as withdrawals and deposits, along with account balances. AR technology and AR reconciliation is performed to make sure that both sets of records, between customers and companies, match.
Final Thoughts: Streamlining AR Reconciliation for Your Business
AR reconciliation is a required process for any business that cares about the accuracy of their financial statements.
With the help of the best AR reconciliation tools, finance and accounting teams can increase their productivity by 85x, maximize their accuracy, and streamline the otherwise time-consuming processes to be able to achieve more.
FAQ
Intelligent reconciliation solution
Intelligent rebate management solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent Financial Automation Solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent financial automation solution
Intelligent regulatory reporting solution
Free up time and reduce errors
Recommended for you

Request a Demo
Book a 30-minute call to see how our intelligent software can give you more insights and control over your data and reporting.

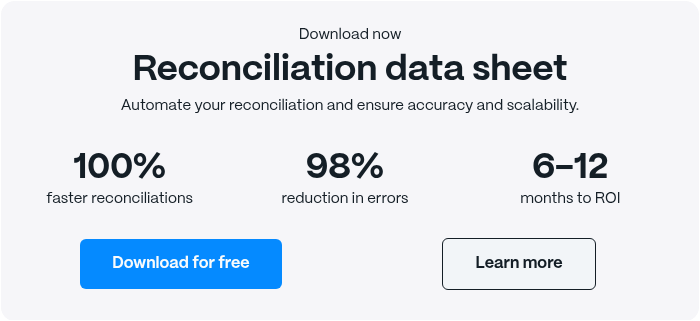
Reconciliation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how to automate your reconciliations for increased accuracy, speed and control.

Regulatory Reporting Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can prepare, validate and submit regulatory returns 10x faster with automation.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Financial Automation Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can run your processes up to 100x faster and with 98% fewer errors.

Rebate Management Data Sheet
Download our data sheet to learn how you can manage complex vendor and customer rebates and commission reporting at scale.

Top 10 Automation Challenges for CFOs
Learn how you can avoid and overcome the biggest challenges facing CFOs who want to automate.
.svg)